| 7th of June 2018 |
|---|
|
| The HI disc of NGC 922 |
| by Elagali et al. |
|
NGC 922 is a collisional ring galaxy located at a distance of 44 Mpc
from our Galaxy. Elagali et al. present new atomic hydrogen (H I)
observations with the Australia Telescope Compact Array which reveal
for the first time the vast extent of the H I disc of this galaxy.
The H I morphology and kinematics of NGC 922 show that it has a
complex interaction history.
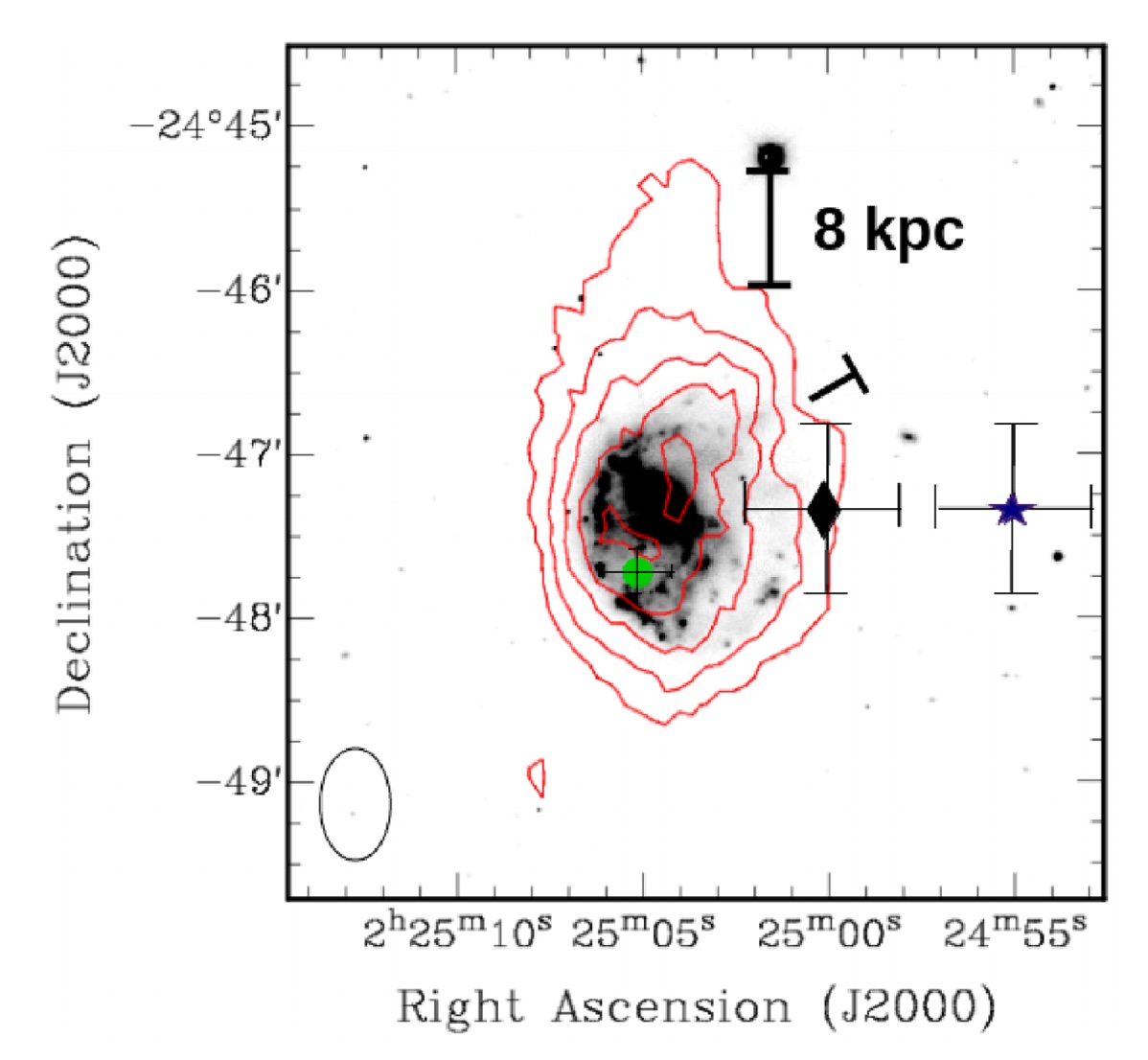
The image shows the ATCA integrated H I column density distribution of NGC 922 superimposed on the optical R-band image obtained from the SINGG (Survey for Ionization in Neutral Gas Galaxies) survey. The column density contours are at (2.3, 4.5, 9.0, 13.5, 18.0) × 10^20 cm−2. The H I centre of this ATCA map is different from the centre of a previous H I map of NGC 922 obtained using the Parkes telescope as part of the HIPASS survey. The ATCA map centre is located exactly at the nucleus of NGC 922, while the HIPASS map centre is denoted by the filled black diamond. The ‘T’ delimits the location of the stellar plume emerging from NGC 922 towards a companion galaxy S2. More details are given in the paper to be published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. |