Go to the source code of this file.
Data Structures | |
| struct | linprm |
| Linear transformation parameters. More... | |
Macros | |
| #define | LINLEN (sizeof(struct linprm)/sizeof(int)) |
| Size of the linprm struct in int units. | |
| #define | linini_errmsg lin_errmsg |
| Deprecated. | |
| #define | lincpy_errmsg lin_errmsg |
| Deprecated. | |
| #define | linfree_errmsg lin_errmsg |
| Deprecated. | |
| #define | linprt_errmsg lin_errmsg |
| Deprecated. | |
| #define | linset_errmsg lin_errmsg |
| Deprecated. | |
| #define | linp2x_errmsg lin_errmsg |
| Deprecated. | |
| #define | linx2p_errmsg lin_errmsg |
| Deprecated. | |
Enumerations | |
| enum | linenq_enum { LINENQ_MEM = 1 , LINENQ_SET = 2 , LINENQ_BYP = 4 } |
| enum | lin_errmsg_enum { LINERR_SUCCESS = 0 , LINERR_NULL_POINTER = 1 , LINERR_MEMORY = 2 , LINERR_SINGULAR_MTX = 3 , LINERR_DISTORT_INIT = 4 , LINERR_DISTORT = 5 , LINERR_DEDISTORT = 6 } |
Functions | |
| int | linini (int alloc, int naxis, struct linprm *lin) |
| Default constructor for the linprm struct. | |
| int | lininit (int alloc, int naxis, struct linprm *lin, int ndpmax) |
| Default constructor for the linprm struct. | |
| int | lindis (int sequence, struct linprm *lin, struct disprm *dis) |
| Assign a distortion to a linprm struct. | |
| int | lindist (int sequence, struct linprm *lin, struct disprm *dis, int ndpmax) |
| Assign a distortion to a linprm struct. | |
| int | lincpy (int alloc, const struct linprm *linsrc, struct linprm *lindst) |
| Copy routine for the linprm struct. | |
| int | linfree (struct linprm *lin) |
| Destructor for the linprm struct. | |
| int | linsize (const struct linprm *lin, int sizes[2]) |
| Compute the size of a linprm struct. | |
| int | linenq (const struct linprm *lin, int enquiry) |
| enquire about the state of a linprm struct. | |
| int | linprt (const struct linprm *lin) |
| Print routine for the linprm struct. | |
| int | linperr (const struct linprm *lin, const char *prefix) |
| Print error messages from a linprm struct. | |
| int | linset (struct linprm *lin) |
| Setup routine for the linprm struct. | |
| int | linp2x (struct linprm *lin, int ncoord, int nelem, const double pixcrd[], double imgcrd[]) |
| Pixel-to-world linear transformation. | |
| int | linx2p (struct linprm *lin, int ncoord, int nelem, const double imgcrd[], double pixcrd[]) |
| World-to-pixel linear transformation. | |
| int | linwarp (struct linprm *lin, const double pixblc[], const double pixtrc[], const double pixsamp[], int *nsamp, double maxdis[], double *maxtot, double avgdis[], double *avgtot, double rmsdis[], double *rmstot) |
| Compute measures of distortion. | |
| int | matinv (int n, const double mat[], double inv[]) |
| Matrix inversion. | |
Variables | |
| const char * | lin_errmsg [] |
| Status return messages. | |
Detailed Description
Routines in this suite apply the linear transformation defined by the FITS World Coordinate System (WCS) standard, as described in
These routines are based on the linprm struct which contains all information needed for the computations. The struct contains some members that must be set by the user, and others that are maintained by these routines, somewhat like a C++ class but with no encapsulation.
Six routines, linini(), lininit(), lindis(), lindist() lincpy(), and linfree() are provided to manage the linprm struct, linsize() computes its total size including allocated memory, linenq() returns information about the state of the struct, and linprt() prints its contents.
linperr() prints the error message(s) (if any) stored in a linprm struct, and the disprm structs that it may contain.
A setup routine, linset(), computes intermediate values in the linprm struct from parameters in it that were supplied by the user. The struct always needs to be set up by linset() but need not be called explicitly - refer to the explanation of linprm::flag.
linp2x() and linx2p() implement the WCS linear transformations.
An auxiliary routine, linwarp(), computes various measures of the distortion over a specified range of pixel coordinates.
An auxiliary matrix inversion routine, matinv(), is included. It uses LU-triangular factorization with scaled partial pivoting.
Macro Definition Documentation
◆ LINLEN
| #define LINLEN (sizeof(struct linprm)/sizeof(int)) |
◆ linini_errmsg
| #define linini_errmsg lin_errmsg |
Deprecated.
- Deprecated
- Added for backwards compatibility, use lin_errmsg directly now instead.
◆ lincpy_errmsg
| #define lincpy_errmsg lin_errmsg |
Deprecated.
- Deprecated
- Added for backwards compatibility, use lin_errmsg directly now instead.
◆ linfree_errmsg
| #define linfree_errmsg lin_errmsg |
Deprecated.
- Deprecated
- Added for backwards compatibility, use lin_errmsg directly now instead.
◆ linprt_errmsg
| #define linprt_errmsg lin_errmsg |
Deprecated.
- Deprecated
- Added for backwards compatibility, use lin_errmsg directly now instead.
◆ linset_errmsg
| #define linset_errmsg lin_errmsg |
Deprecated.
- Deprecated
- Added for backwards compatibility, use lin_errmsg directly now instead.
◆ linp2x_errmsg
| #define linp2x_errmsg lin_errmsg |
Deprecated.
- Deprecated
- Added for backwards compatibility, use lin_errmsg directly now instead.
◆ linx2p_errmsg
| #define linx2p_errmsg lin_errmsg |
Deprecated.
- Deprecated
- Added for backwards compatibility, use lin_errmsg directly now instead.
Enumeration Type Documentation
◆ linenq_enum
| enum linenq_enum |
◆ lin_errmsg_enum
| enum lin_errmsg_enum |
Function Documentation
◆ linini()
| int linini | ( | int | alloc, |
| int | naxis, | ||
| struct linprm * | lin ) |
Default constructor for the linprm struct.
linini() is a thin wrapper on lininit(). It invokes it with ndpmax set to -1 which causes it to use the value of the global variable NDPMAX. It is thereby potentially thread-unsafe if NDPMAX is altered dynamically via disndp(). Use lininit() for a thread-safe alternative in this case.
◆ lininit()
| int lininit | ( | int | alloc, |
| int | naxis, | ||
| struct linprm * | lin, | ||
| int | ndpmax ) |
Default constructor for the linprm struct.
lininit() allocates memory for arrays in a linprm struct and sets all members of the struct to default values.
PLEASE NOTE: every linprm struct must be initialized by lininit(), possibly repeatedly. On the first invokation, and only the first invokation, linprm::flag must be set to -1 to initialize memory management, regardless of whether lininit() will actually be used to allocate memory.
- Parameters
-
[in] alloc If true, allocate memory unconditionally for arrays in the linprm struct.
If false, it is assumed that pointers to these arrays have been set by the user except if they are null pointers in which case memory will be allocated for them regardless. (In other words, setting alloc true saves having to initalize these pointers to zero.)[in] naxis The number of world coordinate axes, used to determine array sizes. [in,out] lin Linear transformation parameters. Note that, in order to initialize memory management linprm::flag should be set to -1 when lin is initialized for the first time (memory leaks may result if it had already been initialized). [in] ndpmax The number of DPja or DQia keywords to allocate space for. If set to -1, the value of the global variable NDPMAX will be used. This is potentially thread-unsafe if disndp() is being used dynamically to alter its value.
- Returns
- Status return value:
- 0: Success.
- 1: Null linprm pointer passed.
- 2: Memory allocation failed.
◆ lindis()
Assign a distortion to a linprm struct.
lindis() is a thin wrapper on lindist(). It invokes it with ndpmax set to -1 which causes the value of the global variable NDPMAX to be used (by disinit()). It is thereby potentially thread-unsafe if NDPMAX is altered dynamically via disndp(). Use lindist() for a thread-safe alternative in this case.
◆ lindist()
Assign a distortion to a linprm struct.
lindist() may be used to assign the address of a disprm struct to linprm::dispre or linprm::disseq. The linprm struct must already have been initialized by lininit().
The disprm struct must have been allocated from the heap (e.g. using malloc(), calloc(), etc.). lindist() will immediately initialize it via a call to disini() using the value of linprm::naxis. Subsequently, it will be reinitialized by calls to lininit(), and freed by linfree(), neither of which would happen if the disprm struct was assigned directly.
If the disprm struct had previously been assigned via lindist(), it will be freed before reassignment. It is also permissable for a null disprm pointer to be assigned to disable the distortion correction.
- Parameters
-
[in] sequence Is it a prior or sequent distortion? - 1: Prior, the assignment is to linprm::dispre.
- 2: Sequent, the assignment is to linprm::disseq.
[in,out] lin Linear transformation parameters. [in,out] dis Distortion function parameters. [in] ndpmax The number of DPja or DQia keywords to allocate space for. If set to -1, the value of the global variable NDPMAX will be used. This is potentially thread-unsafe if disndp() is being used dynamically to alter its value.
- Returns
- Status return value:
- 0: Success.
- 1: Null linprm pointer passed.
- 4: Invalid sequence.
◆ lincpy()
Copy routine for the linprm struct.
lincpy() does a deep copy of one linprm struct to another, using lininit() to allocate memory for its arrays if required. Only the "information to be provided" part of the struct is copied; a call to linset() is required to initialize the remainder.
- Parameters
-
[in] alloc If true, allocate memory for the crpix, pc, and cdelt arrays in the destination. Otherwise, it is assumed that pointers to these arrays have been set by the user except if they are null pointers in which case memory will be allocated for them regardless. [in] linsrc Struct to copy from. [in,out] lindst Struct to copy to. linprm::flag should be set to -1 if lindst was not previously initialized (memory leaks may result if it was previously initialized).
- Returns
- Status return value:
- 0: Success.
- 1: Null linprm pointer passed.
- 2: Memory allocation failed.
◆ linfree()
| int linfree | ( | struct linprm * | lin | ) |
Destructor for the linprm struct.
linfree() frees memory allocated for the linprm arrays by lininit() and/or linset(). lininit() keeps a record of the memory it allocates and linfree() will only attempt to free this.
PLEASE NOTE: linfree() must not be invoked on a linprm struct that was not initialized by lininit().
- Parameters
-
[in,out] lin Linear transformation parameters.
- Returns
- Status return value:
- 0: Success.
- 1: Null linprm pointer passed.
◆ linsize()
| int linsize | ( | const struct linprm * | lin, |
| int | sizes[2] ) |
Compute the size of a linprm struct.
linsize() computes the full size of a linprm struct, including allocated memory.
- Parameters
-
[in] lin Linear transformation parameters.
If NULL, the base size of the struct and the allocated size are both set to zero.[out] sizes The first element is the base size of the struct as returned by sizeof(struct linprm).
The second element is the total size of memory allocated in the struct, in bytes, assuming that the allocation was done by lininit(). This figure includes memory allocated for members of constituent structs, * such as linprm::dispre.
It is not an error for the struct not to have been set up via linset(), which normally results in additional memory allocation.
- Returns
- Status return value:
- 0: Success.
◆ linenq()
| int linenq | ( | const struct linprm * | lin, |
| int | enquiry ) |
enquire about the state of a linprm struct.
linenq() may be used to obtain information about the state of a linprm struct. The function returns a true/false answer for the enquiry asked.
- Parameters
-
[in] lin Linear transformation parameters. [in] enquiry Enquiry according to the following parameters: These may be combined by logical OR, e.g. LINENQ_MEM | LINENQ_SET. The enquiry result will be the logical AND of the individual results.
- Returns
- Enquiry result:
- 0: No.
- 1: Yes.
◆ linprt()
| int linprt | ( | const struct linprm * | lin | ) |
Print routine for the linprm struct.
linprt() prints the contents of a linprm struct using wcsprintf(). Mainly intended for diagnostic purposes.
- Parameters
-
[in] lin Linear transformation parameters.
- Returns
- Status return value:
- 0: Success.
- 1: Null linprm pointer passed.
◆ linperr()
| int linperr | ( | const struct linprm * | lin, |
| const char * | prefix ) |
Print error messages from a linprm struct.
linperr() prints the error message(s) (if any) stored in a linprm struct, and the disprm structs that it may contain. If there are no errors then nothing is printed. It uses wcserr_prt(), q.v.
- Parameters
-
[in] lin Coordinate transformation parameters. [in] prefix If non-NULL, each output line will be prefixed with this string.
- Returns
- Status return value:
- 0: Success.
- 1: Null linprm pointer passed.
◆ linset()
| int linset | ( | struct linprm * | lin | ) |
Setup routine for the linprm struct.
linset(), if necessary, allocates memory for the linprm::piximg and linprm::imgpix arrays and sets up the linprm struct according to information supplied within it - refer to the explanation of linprm::flag.
Note that this routine need not be called directly; it will be invoked by linp2x() and linx2p() if the linprm::flag is anything other than a predefined magic value.
linset() normally operates regardless of the value of linprm::flag; i.e. even if a struct was previously set up it will be reset unconditionally. However, a linprm struct may be put into "bypass" mode by invoking linset() initially with linprm::flag == 1 (rather than 0). linset() will return immediately if invoked on a struct in that state. To take a struct out of bypass mode, simply reset linprm::flag to zero. See also linenq().
- Parameters
-
[in,out] lin Linear transformation parameters.
- Returns
- Status return value:
- 0: Success.
- 1: Null linprm pointer passed.
- 2: Memory allocation failed.
- 3: PCi_ja matrix is singular.
- 4: Failed to initialise distortions.
◆ linp2x()
| int linp2x | ( | struct linprm * | lin, |
| int | ncoord, | ||
| int | nelem, | ||
| const double | pixcrd[], | ||
| double | imgcrd[] ) |
Pixel-to-world linear transformation.
linp2x() transforms pixel coordinates to intermediate world coordinates.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] lin Linear transformation parameters. [in] ncoord,nelem The number of coordinates, each of vector length nelem but containing lin.naxis coordinate elements. [in] pixcrd Array of pixel coordinates. [out] imgcrd Array of intermediate world coordinates.
- Returns
- Status return value:
- 0: Success.
- 1: Null linprm pointer passed.
- 2: Memory allocation failed.
- 3: PCi_ja matrix is singular.
- 4: Failed to initialise distortions.
- 5: Distort error.
Notes:
1. Historically, the API to linp2x() did not have a stat[] vector because a valid linear transformation should always succeed. However, now that it invokes disp2x() if distortions are present, it does have the potential to fail. Consequently, when distortions are present and a status return (stat[]) is required for each coordinate, then linp2x() should be invoked separately for each of them.
◆ linx2p()
| int linx2p | ( | struct linprm * | lin, |
| int | ncoord, | ||
| int | nelem, | ||
| const double | imgcrd[], | ||
| double | pixcrd[] ) |
World-to-pixel linear transformation.
linx2p() transforms intermediate world coordinates to pixel coordinates.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] lin Linear transformation parameters. [in] ncoord,nelem The number of coordinates, each of vector length nelem but containing lin.naxis coordinate elements. [in] imgcrd Array of intermediate world coordinates. [out] pixcrd Array of pixel coordinates. Status return value: - 0: Success.
- 1: Null linprm pointer passed.
- 2: Memory allocation failed.
- 3: PCi_ja matrix is singular.
- 4: Failed to initialise distortions.
- 6: De-distort error.
Notes:
1. Historically, the API to linx2p() did not have a stat[] vector because a valid linear transformation should always succeed. However, now that it invokes disx2p() if distortions are present, it does have the potential to fail. Consequently, when distortions are present and a status return (stat[]) is required for each coordinate, then linx2p() should be invoked separately for each of them.
◆ linwarp()
| int linwarp | ( | struct linprm * | lin, |
| const double | pixblc[], | ||
| const double | pixtrc[], | ||
| const double | pixsamp[], | ||
| int * | nsamp, | ||
| double | maxdis[], | ||
| double * | maxtot, | ||
| double | avgdis[], | ||
| double * | avgtot, | ||
| double | rmsdis[], | ||
| double * | rmstot ) |
Compute measures of distortion.
linwarp() computes various measures of the distortion over a specified range of pixel coordinates.
All distortion measures are specified as an offset in pixel coordinates, as given directly by prior distortions. The offset in intermediate pixel coordinates given by sequent distortions is translated back to pixel coordinates by applying the inverse of the linear transformation matrix (PCi_ja or CDi_ja). The difference may be significant if the matrix introduced a scaling.
If all distortions are prior, then linwarp() uses diswarp(), q.v.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] lin Linear transformation parameters plus distortions. [in] pixblc Start of the range of pixel coordinates (i.e. "bottom left-hand corner" in the conventional FITS image display orientation). May be specified as a NULL pointer which is interpreted as (1,1,...). [in] pixtrc End of the range of pixel coordinates (i.e. "top right-hand corner" in the conventional FITS image display orientation). [in] pixsamp If positive or zero, the increment on the particular axis, starting at pixblc[]. Zero is interpreted as a unit increment. pixsamp may also be specified as a NULL pointer which is interpreted as all zeroes, i.e. unit increments on all axes.
If negative, the grid size on the particular axis (the absolute value being rounded to the nearest integer). For example, if pixsamp is (-128.0,-128.0,...) then each axis will be sampled at 128 points between pixblc[] and pixtrc[] inclusive. Use caution when using this option on non-square images.[out] nsamp The number of pixel coordinates sampled.
Can be specified as a NULL pointer if not required.[out] maxdis For each individual distortion function, the maximum absolute value of the distortion.
Can be specified as a NULL pointer if not required.[out] maxtot For the combination of all distortion functions, the maximum absolute value of the distortion.
Can be specified as a NULL pointer if not required.[out] avgdis For each individual distortion function, the mean value of the distortion.
Can be specified as a NULL pointer if not required.[out] avgtot For the combination of all distortion functions, the mean value of the distortion.
Can be specified as a NULL pointer if not required.[out] rmsdis For each individual distortion function, the root mean square deviation of the distortion.
Can be specified as a NULL pointer if not required.[out] rmstot For the combination of all distortion functions, the root mean square deviation of the distortion.
Can be specified as a NULL pointer if not required.
- Returns
- Status return value:
- 0: Success.
- 1: Null linprm pointer passed.
- 2: Memory allocation failed.
- 3: Invalid parameter.
- 4: Distort error.
◆ matinv()
| int matinv | ( | int | n, |
| const double | mat[], | ||
| double | inv[] ) |
Matrix inversion.
matinv() performs matrix inversion using LU-triangular factorization with scaled partial pivoting.
- Parameters
-
[in] n Order of the matrix ( 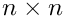
[in] mat Matrix to be inverted, stored as mat[ 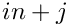
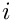
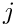
[out] inv Inverse of mat with the same storage convention.
- Returns
- Status return value:
- 0: Success.
- 2: Memory allocation failed.
- 3: Singular matrix.
Variable Documentation
◆ lin_errmsg
|
extern |
Status return messages.
Error messages to match the status value returned from each function.
Generated on for WCSLIB by