Radio Astronomy at Dover Heights
Jessica Chapman, CSIRO
- Introduction
- Astronomers at Dover Heights
- Yagi Antennas at Dover Heights
- Sea Interferometry
- Radio Waves from the Sun and Nebulae
- Radio Waves from Galaxies
- The Hole-in-the ground Antenna
- The Dover Heights Memorial
- Further Reading
Introduction
Rodney Reserve, on the cliff tops at Dover Heights in the eastern suburbs of Sydney, was one of the most remarkable and important astronomical sites in New South Wales.
In the later years of the second world war the Dover Heights site was used by the Australian Army as a coastal defence radar station. The site was also used by scientists from the CSIRO Division of Radiophysics (at that time known as the CSIR) for experimental radar work. After the war ended, the Division of Radiophysics developed the site as a field station for radio astronomy.
In the mid-1940s almost nothing was known about radio waves from space. From 1946 to 1954 scientists and engineers from the CSIRO Division of Radiophysics built a range of radio telescopes at Dover Heights and developed new ways of collecting radio data. Many major discoveries were made at Dover Heights. These established Australia as a world leader in the emerging new science of radio astronomy.
The Dover Heights discoveries revolutionised space exploration and heralded a new era in astronomy. By looking at the radio waves emitted from objects in space, we can probe deeper and reveal the very distant universe. Since the first discoveries at Dover Heights, radio waves have been used to explore the entire cosmos, from the Sun and planets in our solar system, to stars and gas in our Galaxy, and beyond to other galaxies and the most distant reaches of the Universe.
Astronomers at Dover Heights
Some of the scientists and engineers who worked at Dover Heights included John Bolton, Bruce Slee, Gordon Stanley, Kevin Westfold and Dick McGee. They belonged to the radio astronomy group at the CSIRO Division of Radiophysics. Other people in this group worked at a number of field stations around New South Wales. The group was led by Joe Pawsey, while Taffy Bowen was the Chief of the Division.
Yagi Antennas at Dover Heights
Many astronomical observations at Dover Heights were carried out using Yagi antennas that were initially constructed using left over materials from the second world war. In 1946 the first simple Yagis were mounted on the roof of the WWII block house. As shown in the pictures below, successively more elaborate Yagi antennas were built and these were used to survey the sky for sources of radio emission.
Sea Interferometry
Several of the Yagi antennas at Dover Heights were used to take radio observations using a special technique known as sea interferometry. In this technique, the antenna detects radio waves that come directly from a source in the sky. At the same time it detects other radio waves from the source that are reflected off the sea. The two sets of waves are combined and give an 'interference' pattern. The strength and size of the source can be measured from the intensity fluctuations recorded on the interference patterns. These were recorded on paper charts.
Radio Waves from the Sun and Nebulae
The Sun was the first object observed with the radio telescopes at Dover Heights. Strong bursts of radio emission were received during times of sunspot activity.
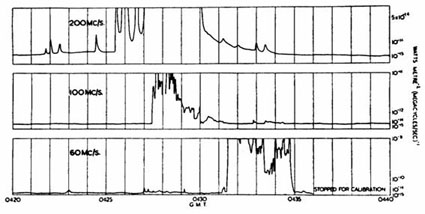
When the radio telescopes were pointed towards the sky they revealed areas of concentrated radio emission. Further investigations showed that the radio waves came from gas clouds in our Galaxy. One of the earliest detections was the radio emission from the supernova remnant known as the Crab Nebula.
Radio waves from Galaxies
More than 110 sources of radio emission were discovered using the radio telescopes at Dover Heights. A wonderful and unexpected discovery was that many distant galaxies are hugely powerful sources of radio waves. We now know that in some galaxies the radio waves are generated by black holes that are hundreds of millions of times more massive than the Sun. The first extragalactic radio sources to be identified as galaxies were Virgo A, Centaurus A and Cygnus A, all millions of light-years away.
What is a radio galaxy?
Galaxies contain billions and billions of stars just like our sun. At night we can see the galaxy that we live in stretching across the sky - we call it the Milky Way. Many galaxies contain massive black holes at their centres, sometimes weighing billions of times more than our sun.
In some galaxies these black holes are sucking in the material around them, spinning it up fast and then squirting it away from the black hole at close to light speed, as a jet. These jets produce radio waves that radio telescopes like the one that was operating at Dover Heights can detect - galaxies such as these are called radio galaxies.
On the left hand side is a complete image of the radio emission from the Centaurus A radio galaxy (made by the "Dish" at Parkes). The other images in the picture, moving from left to right, zoom in closer and closer to the black hole that lies at the centre of the radio galaxy. In the last images you can see the jet of material being produced from near the black hole.
The Hole-in-the-Ground Antenna
In 1951, the leading radio astronomers at Dover Heights, John Bolton, Gordon Stanley and Bruce Slee, wanted a more powerful instrument than the 12-Yagi array, but the CSIRO Division of Radiophysics could not supply the necessary funding. They therefore decided to build a new radio telescope themselves, using a novel design. With considerable ingenuity, they spent their lunchtimes, over a three-month period excavating a 21.9-m diameter dish-shaped hole in the sand a little to the north-west of the block house. The surface was consolidated with ash, metal strips from packing cases were laid across the surface to provide reflectivity, and a mast with a dipole was erected at the centre of the antenna in order to receive the reflected radio signals. This instrument was the second-largest radio telescope in the world at the time, and by using the rotation of the Earth and altering the positioning of the aerial mast it was possible to observe different regions of the sky.
After Bolton, Stanley and Slee demonstrated that the design concept worked, the `hole-in-the ground' antenna was extended, in 1953, to a diameter of 24.4 metres and the surface was coated with concrete and lined with wire mesh to provide a reflecting surface.
This radio telescope was used to survey the sky for radio sources, and for a detailed study of a strong radio source that was detected in the constellation of Sagittarius. The radio astronomers realised that this source (called Sagittarius A) was located at the very centre of our Galaxy! These observations gained further fame for Australia and Dover Heights when in 1958 the International Astronomical Union decided to adopt the position of Sagittarius A as the coordinate centre for the system of galactic `latitude' and `longitude' that is still used today by all astronomers.
In 1954 the focus of the Division of Radiophysics shifted to the Fleurs field station, and the Dover Heights facility was closed down, bringing to an end a remarkable decade of scientific breakthroughs and achievement. More than any other field station, Dover Heights helped establish Australia's reputation as the world's leading nation in the emerging field of radio astronomy.
The Dover Heights Memorial
To celebrate the history and achievements of the Dover Heights site, the Australia Telescope National Facility, with support from the Waverley Council, has installed a scientific memorial at Rodney Reserve on the original site. This includes a full-size replica of the 8-element Yagi used in 1951 and a display panel with detailed information. The memorial was opened on 20 July 2003 by Her Excellency, Professor Marie Bashir, Governor of New South Wales. The opening ceremony was timed to coincide with a General Assembly meeting of the International Astronomical Union, and many distinguised radio astronomers from around the world attended.
Further Reading
Here are some references for further reading.
Bolton, J., 1982. Radio astronomy at Dover Heights. Proceedings of the Astronomical Society of Australia, 4, 349-358.
Orchiston, W., 2004. From the solar corona to clusters of galaxies: the radio astronomy of Bruce Slee. Publication of the Astronomical Society of Australia, 21, 23-71.
Orchiston, W., and Slee, B., 2002. Ingenuity and initiative in Australian radio astronomy: the Dover Heights 'hole-in-the-ground' antenna. Journal of Astronomical History and Heritage, 5, 21-34.
Pain, S., 2003. Two men and a wheelbarrow. New Scientist, 13 September: 50-51.
Slee, O.B., 1994. Some memories of the Dover Heights field station, 1946-1954. Australian Journal of Physics, 47, 517-534.
Stanley, G.J., 1994. Recollections of John G. Bolton at Dover Heights and Caltech. Australian Journal of Physics, 47, 507-516.
