|
ATNF Pulsar Catalogue Tutorial Pages: Introduction 1: The simplest query 2: Using the standard parameter set 3: Defining your own display parameters 4: Sorting 5: Conditional logic statements 6: Filtering on pulsar names 7: Finding pulsars within a circular region 8: Formatting the output 9: Obtaining the plotted output 10: Playing with the applet 11: Using the expert parameters |
Circular Boundary Page 7: Finding pulsars within a circular region It might be interesting to look at pulsars that are close to, say, another pulsar or supernova remnant. With such a need, the pulsar catalogue allows you to specify a circular region in space and obtain all the pulsars that fall within this net. Before trying out the example, make sure that you click on the "Clear All" button located at the top and bottom of the form. This resets the entire form to its initial default values. Then check the "Name", "JName", "RaJ" and DecJ" checkboxes in the Display parameters input section. In the input field called "Within circular boundary" located near the bottom of the form, leave the coordinate units as "raj/decj" (referring to right ascension and declination) and use a radius of 2 degrees. Type for the circle's centre coordinate as "19 33" for the raj and in the second text box (referring to the decj) type in "16". This query will find all pulsars that lie within the circle with center (19:33 raj, 16 decj) with radius of 2 degrees. Click on the "Table" submit button and you should have the following output along with its input: 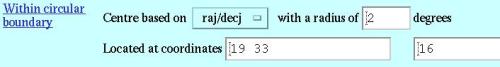
 As you can see from the output, all the pulsars there have BNames close to 1933 (19:33 raj) and 16 (16 decj). Because of the differing ways in which astronomers write coordinates, the input text field for the coordinates may also contain ":" instead of " " as a delimiter between the hours/degrees, minutes and seconds. For example, instead of "19 33 12" you can type in "19:33:12". As a final lesson on the text/tabular output option of the pulsar catalogue, the next lesson will involve the different output styles available as well as some other formatting options available. Click on the "Back" button of your browser and then click on the "Clear All" button at the top/bottom of the page so the form is ready for the next lesson. next page >> |
This loads a font easier to read for people with dyslexia.
This renders the document in high contrast mode.
This renders the document as white on black
This can help those with trouble processing rapid screen movements.
