


 Karma Home Page
Karma Home Page
Next: 4 Viewing Images and
Up: Karma User Manual
Previous: 2 Common Features
The <kvis> programme allows you to view multiple
datasets.
This tool allows you to compare different datasets in a very easy
fashion. You can display any dataset as an image, overlay contours of
datasets, show profiles along any axis, and much more. The programme
uses the ImageDisplay widget (section 2.15) to
provide the usual interface.
The tool is centred around the concept of a blink-state, which
defines how you want to display datasets (i.e. which dataset is shown
as the image, which datasets are shown as contours, how to control
movies and profiles and so on). A blink-state can control the display
settings of all datasets that have been loaded into the application.
Multiple blink-states may be created, each with a different
configuration of what datasets are to be shown. By pressing a key, the
display is switched from one blink-state to another.
Blink-states are created and managed using the DataBrowser
widget.
Pressing the View button will pop up the ViewDatasets
widget.
This widget provides controls for a display window to manage the
display of multiple datasets. Most of the controls for data display
management are in the DataBrowser widget.
The controls provided are:
- Close this will close the window
- Browsers this will pop up the data browser window(s) for
this display window
- Movie this will pop up the AnimateControl widget
(section 2.3), which will allow you to play movies
and step through frames. In addition, the following key bindings are
defined for the main display window:
- PgDn go to previous frame
- PgUp go to next frame
- Home go to start frame
- End go to end frame
On some keyboards, PgDn is marked as Next and PgUp
is marked as Prev.
- Profile Mode Menu this allows you to pop up the
TracePopup widget (section 2.11) and choose the
profile mode. The following modes are available:
- Slice Direction Menu this allows you to choose how you
want to slice your cube. You can view XY, XZ or ZY planes
- Profile Axis Menu this allows you to choose along which
axis you want the profile to be displayed (valid only for line profile
mode)
- Freeze Displayed Intensity Range if unset (the default),
the intensity range specified for a dataset is used when that dataset
is displayed as an image. If set, switching from one dataset to the
next will not change the displayed intensity range (however, changing
the intensity range for the image dataset will change the displayed
intensity range)
- Track Cursor if set, the corresponding image display
window will ``listen'' for cursor moves which occur in other image
display windows, and will draw a red circle at the same world
co-ordinate position
- Show Frame in Line Profile if this is set the current
frame displayed in the main image window is shown as a vertical red
line in the profile window. This marker is only drawn if the profile
axis is the unseen axis
- Auto Title if enabled, the axis labelling title is
automatically generated. Whenever this is disabled, the string
specified by Axis Labelling Title is used instead
- Show Beam if enabled, the dataset headers are searched for
``BPA'', ``BMAJ'' and ``BMIN'' FITS-style keywords. If these keywords
are present, a representation of the telescope beam is overlaid on the
image
- Show Beam Name if enabled, the name of the dataset is
placed near the beam representation
- Beam Xpos controls the horizontal position of the
the beam
- Beam Ypos controls the vertical position of the
the beam
In addition, if you click the left mouse button in the display window
without moving it in between the press and release, the image will pan
across. If you click the middle mouse button, the image will zoom in
2x (the new centre of the image will be the place where you
clicked). Click the right mouse button to zoom out 2x. If the profile
mode is ``box'' then you can't use the middle mouse button to zoom.
Pressing the c key in the display window will compute and
display a scatter plot of intensity values in the image dataset versus
intensity values in the ``alternate'' dataset. This is useful for
seeing if there is a correlation between the values in two images. You
can use the left mouse button to define a sub-image (similarly to
zooming in) from which the scatter plot is computed.
A screen snapshot is available
here.
This widget provides controls for managing the display of multiple
datasets.
A screen snapshot is available
here.
The controls provided are:
- Close this will close the window
- Destroy the blink-state that the browser is showing is
destroyed. It is not possible to destroy the first blink-state for the
display window
- Copy create a new blink-state (and browser) which has the
same configuration as the currently viewed blink-state. In all
mode, the browser for the new blink-state is popped up
- Show menu gives control over how the various blink-states
are displayed. The following modes are available:
- all each blink-state is viewed in its own browser
- some each display window has a single browser, which can
be switched to display any blink-state for the display window
- Data menu selects which kind of data is displayed in the
browser. The choices are:
- Arrays gridded array data (can be viewed as images or
contours)
- Annotations text and geometric figures which can be
overlaid for annotation purposes
- Advanced this will raise the
advanced control panel
- Make Data this will raise the
make data control panel
Beneath these general controls, the list of loaded data appears. Each
line shows the name and a summary of the configuration settings for
that dataset. The list section is different for each data type. There
are common operations that may be performed irrespective of data type,
which are described here.
There is always a highlighted line, which shows which entry you can
make changes to (using either the mouse buttons or the keyboard). The
highlighted line is shown by a slightly different background
colour. You can change the highlighted line by using the mouse or
up/down arrow keys.
There is also a selected line, which shows which entry has more
detail shown in the section(s) below. The list section only shows a
summary of the current configuration for each dataset. The selected
line is shown by using reverse video.
If the browser is in active mode (the default), then the
selected line is locked to the highlighted line. If in passive
mode, the selected line does not move until you explicitly
select an entry.
If you select an entry while in active mode, the browser
switches to passive mode. If in passive mode and you
select the already selected entry, the browser switches to
active mode.
As the mouse is moved over the data names, one of the names will be
highlighted. The mouse and keyboard may be pressed to control the
settings of the highlighted data. The following bindings are
available:
- Left Mouse select the highlighted dataset for display in
the sections below, and disable active mode. If the data is
already selected and active mode is disabled, active mode is
enabled
- Spacebar same effect as left mouse button
- Up Arrow highlight and select the previous data
- Down Arrow highlight and select the next data
- = (equals sign) selects this dataset for
replacement, copying all data
attributes
-
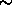 (tilde sign) selects this dataset for
replacement without attribute copying
(tilde sign) selects this dataset for
replacement without attribute copying
There are other key bindings which are independent of which dataset
the mouse is highlighting:
- Left Arrow cycle backwards in the list of blink-states for
the same window (in Some or One modes). Has no effect in
All mode)
- Right Arrow as above, but cycle forwards
- Shift Left Arrow similar to Left Arrow, but also
make the blink-state active
- Shift Right Arrow similar to Right Arrow, but also
make the blink-state active
- Control Left Arrow cycle backwards to the last browser
for the previous display window (One mode). Has no effect in
other modes
- Control Right Arrow cycle forwards to the first browser
for the next display window (One mode). Has no effect in
other modes
- Shift Control Left Arrow similar to Control Left
Arrow, but also make the blink-state active
- Shift Control Right Arrow similar to Control Right
Arrow, but also make the blink-state active
- b key blink the display window to the next browser for
this display window
- B key make the currently viewed blink-state active
- > key blink the display window to the next browser for
this display window
- < key blink the display window to the next browser for
this display window
The list section will show single character codes in a number of
columns to the left of the data entry names. Different data types will
show a different number of columns, and the character codes have
different meanings as well. However following convention is followed:
- = (equals sign) this dataset has been selected for
replacement with data attribute
copying
-
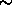 (tilde sign) this dataset has been selected for
replacement without attribute copying
(tilde sign) this dataset has been selected for
replacement without attribute copying
- uppercase this is an exclusive option: only one entry may
have this option set per blink-state
- lowercase non-inclusive option. Any number of entries may
have this option set
Below the list of data, more detailed information and configuration
settings are shown. The appearance depends on the kind of data being
shown.
The configuration controls for the different data types are described
below.
As discussed above, a dataset may be selected for replacement.
When a new dataset is loaded, the list of already loaded datasets is
scanned for a dataset which has been selected for replacement,
and was loaded from the same data source. A typical data source is a
file browser, but may also include network connections. When a dataset
is replaced with a new one, either all the old settings (such as
intensity range, contour levels, etc.) are retained or none of the
settings are retained, depending on which replacement mode was
selected.
If more than one dataset is selected for replacement, and these
datasets were loaded from the same data source, the selected dataset
closest to the top of the list is replaced.
Note that if a data source is removed (e.g. a file browser is
destroyed), then datasets loaded via that data source can no longer be
replaced. These datasets can still be explicitly unloaded, however.
There are several columns used to display a summary of the
configuration, using a simple legend. These are described below:
- Image Column shows which dataset(s) contribute to the
displayed image. These are exclusive settings. The legend is:
- I show this array as the image
- A this array is the "alternate image" for
intensity-intensity scatter plot computation
hue-intensity
- Contour Column shows which datasets are displayed as
contours. These are non-exclusive settings. The legend is:
- c show this array as a normal contour map
- r show this array as a Renzogram (only for cubes)
- Movie Column shows which datasets can be shown as a
movie. The legend is:
- M enable movie controls for this array
- m slave this array to the movie controls
- Profile Column shows which datasets can be shown as
profiles. The legend is:
- P display line profiles of this array (this array controls
the axis labelling and is drawn on top)
- p display line profiles of this array
The following keyboard and mouse bindings are available to quickly
control the configuration:
- Middle Mouse show as the image, the previous image becomes
the "alternate image". If already displayed as the image, disable
image display
- Right Mouse toggle between enabling and disabling contour
display
- i key same effect as the middle mouse button
- control-i make the next dataset in the list the currently
displayed image. This will cycle back to the top of the list when the
end is reached
- control-shift-i make the previous dataset in the list the
currently displayed image. This will cycle back to the end of the list
when the top is reached
- a key make this image the "alternate image"
- c key same effect as the right mouse button
- r key toggle between enabling and disabling Renzogram
display
- control-c enable contours and apply levels
- control-r enable Renzogram and apply level
- M key enable movie controls for this array
- m key slave this array to the movie controls
- P key display line profiles of this array (this array
controls the axis labelling and is drawn on top)
- p key display line profiles of this array
This shows information about the array, such as the directory from
where the array was loaded, the format of the data (i.e. FITS, AIPS,
Miriad, Gipsy and many more), the size and dimensionality and the
range of data values. The following control buttons are available:
- Histogram pop up a histogram for this array. The histogram
display can be used to control the intensity range for this array
- Clone create a virtual copy of the array, which will have
independent configuration settings. Note that the data are not copied,
instead a reference is made
- Unload unload the array
Note that these operations affect all browsers/blink-states and all
display windows.
How to display an array is controlled via this section. Some controls
are per blink-state, while others are global and apply to all
blink-states and all display windows. The following controls are per
blink-state:
- Image menu. The choices are:
- off the array is not selected for image display
- main the array is selected for normal image display
- alt the array is the ``alternate'' image for computing
intensity-intensity scatter plots
- Contour menu. The choices are:
- off the array is not displayed as contours
- map the array is shown as normal contours
- renzo the array is shown as a ``Renzogram''
- Movie menu. The choices are:
- off the array will not be shown as a movie
- master the array is shown as a movie and controls the
frames
- slave the array is shown as a movie and is slaved to the
master
The following controls are global to the application, and affect all
blink-states and display windows:
This control panel allows you to control some extra aspects of the
behaviour of all data browsers. The following controls are available:
- Close this will close the window
- Clip Mode menu controls how changes in the low and high
clip levels affect display windows. The following modes are available:
- Image and Profiles the image intensity range and profile
vertical range are synchronised and clip level changes affect both
- Images only only the image intensity range is affected by
clip level changes
- Profiles only only the profile vertical range is affected
by clip level changes
- Both later the image intensity range and profile
vertical range are affected by subsequent clip level changes, but they
are not immediately synchronised
- Range changes affect all arrays if this is turned on, an
attempt to change the clip levels of any array dataset will change the
clip levels for all array datasets
- Make slaved movie on load if this is turned on, an array
dataset with three or more dimensions will be automatically marked as
a movie slave when loaded
- Activate annotations on load if this is turned on, an
annotation dataset is automatically made active (i.e. displayed) when
loaded
- Slave Profile H-range to image window if this is turned
on, the horizontal range of the profile window is set to the same
as the horizontal range of the image window if the the axes correspond
- Show new data as Image if this is turned on, an array
dataset is marked as the active image when loaded
This control panel allows you to create new array data from existing
array data. This is useful if you want to combine data together. The
following controls are available:
- Close this will close the window
- Algorithm menu controls how data arrays are combined. The
following modes are available:
- RGB combine one, two or three datasets into an RGB (red,
green and blue) array. Each colour component is 8 bits, yielding a 24
bit array. The input values between the low and high clip are linearly
scaled into the output. If the clip values on an input array are
subsequently changed, the RGB image is rescaled. The following
bindings are available:
- R use this dataset as the red colour component
- G use this dataset as the green colour component
- B use this dataset as the blue colour component
- Left Mouse use this dataset as the red colour component
- Middle Mouse use this dataset as the green colour component
- Right Mouse use this dataset as the blue colour component
- # use this dataset as the grid template
- Arithmetic combine multiple datasets using simple
arithmetic (addition, subtraction, multiplication or division). The
output dataset is computed by processing the list of datasets from top
to bottom, applying the specified arithmetic operations for selected
datasets. Before processing any datasets, the output dataset is
initialised to either zeros (if the first operator is addition or
subtraction) or ones (if the first operator is multiplication or
division). The following bindings are available:
- + add this dataset to the output dataset
- - subtract this dataset from the output dataset
- * multiply the output dataset by this dataset
- / divide the output dataset by this dataset
- Hue Intensity combine two datasets into a Hue-Intensity
array. The two datasets may be directly mapped to intensity and hue,
or they can represent a complex image. The real and imaginary
components will be in separate datasets and they are converted to
amplitude and phase values, which are then mapped to intensity and
hue. The following bindings are available:
- B use this dataset as the brightness (intensity) component
- H use this dataset as the hue (colour) component
- R use this dataset as the real component
- I use this dataset as the imaginary component
- Left Mouse use this dataset as the brightness component
- Middle Mouse use this dataset as the hue component
- Right Mouse use this dataset as the grid template
- # use this dataset as the grid template
- the dataset list shows the available datasets. This is used to
mark which datasets are used as inputs to the combining process. This
list has a similar interface as the dataset list in the data
browser. Note that in most cases, a dataset can only be marked
once. If you need to mark a dataset for multiple purposes (such as to
use it for both red and green inputs), you will need to clone the
dataset first
- Name this allows you to specify the name for the new
dataset. A default name is provided
- Make this will create the new dataset, based on the
selections you have made. This could take some time, depending on how
large the input datasets are
There is just one column used to display a summary of the
configuration. The a character is used to indicate whether a
annotation file is active (visible) or not. The a key may be
used to switch between the two states. The middle mouse button has the
same effect of switching between the two states.
This shows where directory from which the annotation file was
loaded. the Unload button may be used to unload the annotation
file. This affects all blink-states and display windows.
The Active toggle may be used to switch between active (visible)
and inactive settings for this annotation file.
You may pass the names of files to be loaded via the command-line. You
may specify as many files as you desire, up to the limit imposed by
the operating system.
Earlier in this chapter (3.2) is a brief
description of how you can use the c key to compute and display
an intensity-intensity scatter plot of two images. You may also use
this facility to display a scatter plot of two channels from the same
cube. Simply clone the cube (i.e. using the Clone data
browser button), and select the two channels, one from each cube. You
will need to ensure that the original and cloned cube do not have a
master/slave movie relationship.
If there is a master/slave movie relationship, then the scatter plot
is computed using the two frames which have corresponding co-ordinates
for the frame axes. This is usually the desired setting when
generating scatter plots from frames of two different cubes.
Note that when computing a scatter plot from two images with a
different co-ordinate grid, the pixels from the unseen image
correspond to pixels with the same world co-ordinates in the visible
image. Thus, there is no need to re-grid either of the images.
A ``renzogram'' is a technique for displaying velocity information in
a cube in a different (better) way than velocity fields. The technique
was pioneered by Renzo Sancisi at the Kapteyn Institute in Groningen.
A ``renzogram'' overlays a single-level contour map for every channel
in a cube over an image (such as an optical image or moment map). The
contour map for each channel is displayed in a different colour
(typically red-blue, although this can be changed interactively). This
has an advantage over velocity fields because it shows multiple peaks
in the velocity profile, which a velocity field cannot do.
To use this feature, simply load a cube and select it for renzogram
display in the data browser. You can control the contour level used
for the renzogram, and the range of channels displayed.
You may wish to load a separate image (perhaps an optical image) and
display that as the image. This can be useful for comparing optical
and radio data.
You can also view a profile (spectrum) of your
cube. Just select select line profile display and a profile window
will appear. You will note that the profile is drawn in the same
colours as the contours.
A screen snapshot of the older <krenzo> programme is available
here



 Karma Home Page
Karma Home Page
Next: 4 Viewing Images and
Up: Karma User Manual
Previous: 2 Common Features
Richard Gooch
Mon Aug 14 22:25:04 PDT 2006